The Simulation Code and Teacher Password was provided to you during purchase. Please check your registered e-mail.

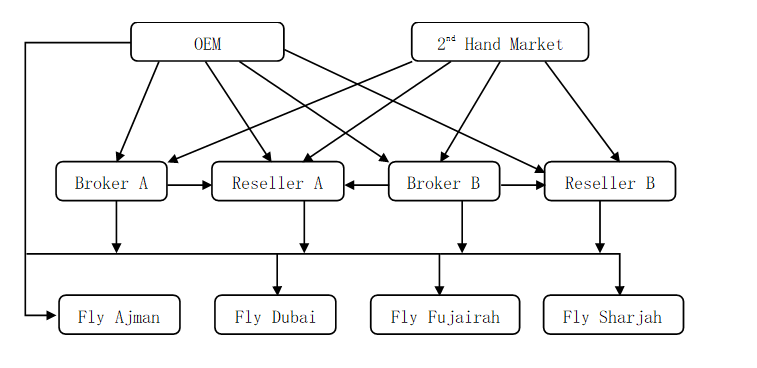
Players in aero-supply network ecosystem negotiate on terms (price, quality, & delivery schedule) of the deal, within the regulatory framework, and often along the sidelines of RAK Aero-parts Brokers & Resellers Association (RABRA) conferences and Association of Propeller-Aircraft Operators (APO) meetings that happen from time to time.
The spart parts from the second-hand market are usually sold at a discount. However, there is a floor price set by the second-hand market. Used parts of 70% quality rating have a floor price of 50% of OEM price. Used parts of 85% quality rating have a floor price of 60% of OEM price. Like the OEM market, there is a supply constraint of 2 x OEM supply from the second-hand market per quarter, split at 50:50 quantity for 70% and 85% quality rated parts respectively.
There are 'n' number of Brokers and Resellers in the market. A broker may charge a percentage commission from any seller, and mark up the commission in the price of any deal that the broker facilitates with a willing buyer. The broker's markup (commission) is equally shared by the buyer and seller at the time of transaction. A broker has to charge a minimum of 1 percent commission for any transaction that the broker facilitates.
A reseller may buy equipment from OEM or second-hand market or another re-seller and sell it to any willing buyer (air operator on another reseller). Resellers unlike brokers have warehousing facilities and can stock inventory up to 3 numbers of spares.
Aircraft operators have quarterly requirement of spares. Usually, requirements vary between 2 to 4 spare parts per quarter. For example, an airline operator may need 2 components with 100% quality rating, and 1 component with 75% (or better) quality rating. If the spare requirements are not met in any quarter, the civil aviation regulator imposes a penalty on the aircraft operator by downgrading the average fleet quality rating of the operator. Each aircraft operator attracts customers commensurate to the quality rating of the fleet.
The buyers, sellers or enablers in the aero-supply network are only allowed to make spot market sales and forbidden from entering into forward contracts. All contracts can be made only on the basis of confirmed stocks in seller's inventory, that are available for delivery honoring any contracts made.
Each player in the aero-supply network seeks to be the dominant player (node) in the aero-supply network. While this may be generally measured by the volume of business, the objectives and winning criteria for players in different echelons (levels) in the supply network are different as stated below:
While each player competes against each other for best deals, RABRA and APO meet once in a year to co-operate on collective bargaining strategies. Hotlines are established (see chat box online) for individual communication with players, as well as open communication with peers in RABRA or APO, as the case may be.
Good Luck!
